The two types of application architecture commonly used are:
1. Monolithic architecture and
2. Microservices architecture
Let’s take a sneak peek into both types of architecture.
Monolithic architecture
Monolithic architecture is the traditional way of application development. The applications built with monolithic architecture have a single code base and multiple modules. In fact, monolithic applications are built as a single package with all the components and services included in it. They are a full package inclusive of a database, client-side user interface, and a server-side application. Here, all the components of the program are interconnected and interdependent.
Scaling monolithic applications is easy and simple.
Microservices architecture
Microservices architecture is a service-based application development technique. In microservices architecture, an application is divided into different components which are developed, packaged and deployed individually through individual processes. These components are known as services. Thus, a microservices architecture can be thought of as a collection of many small, autonomous services.
Each service represents a functionality of the application which can be developed individually. All these services can communicate with each other via APIs.
Microservices architecture pattern is specially designed for cloud-based hosting.
When and Why to use Microservices architecture?
Microservices architecture for application is mainly used to support continuous delivery.
However, it is preferable to use when:
- The application will have a high volume of traffic or transaction
- The project is of long-term.
- Modularisation and code re-usability is the main priority
- Specific areas of the application need to be scaled on demand.
Many company giants like Amazon, Walmart, Netflix and eBay are using this architecture.
Pros and Cons
PROS:
Small in size:
Microservices is where each service performs only one business task. Hence, it will be small in size and easy to maintain than any other monolithic application.
Focused:
Each microservice is designed to deliver only one business task. While designing a microservice, the architect should be concerned about the focal point of the service, which is its deliverable. By definition, a microservice should be full stack in nature.
Each of these microservice can be developed individually. This helps the developing teams to completely focus on one service at a time. Moreover, the smaller scope of each service makes the code base easier to understand.
Technology Heterogeneity:
Microservice supports different technologies to communicate with each other in one business unit, which helps the developers to use the correct technology at the correct place. By implementing a heterogeneous system, one can obtain maximum security, speed and a scalable system.
Independent deployments:
As a result, continuous deployment is possible without affecting other components of the architecture. This means that unlike monolithic architecture, you don’t need to redeploy the entire application again for small changes.
Resilience:
Microservices follows a high level of resilience in building methodology. Hence, whenever one unit fails it does not impact the entire business.
Granular Scaling:
Each service can be scaled individually too. So, the deployment of the required instances for the satisfaction of particular services also becomes easy. Moreover, you can also choose the best hardware for a particular service.
CONS:
Requires skilled professionals:
Due to technological heterogeneity, different technologies can be used to develop different components of a microservice. A huge set of skilled professionals is required to support this big heterogeneous distributed software. Hence, the distributed system stands as the topmost disadvantage of using a microservices.
Expensive:
You will have to maintain different server space for different business tasks which makes it costly.
Difficulty in management:
As different languages and frameworks are used to develop different components of the application, it becomes difficult to manage the application. Furthermore, use of different technology stack leads to non-uniform application architecture. This may increase the maintenance cost in the long run.
Versioning problem:
Though microservices gives an ease in deployment, care should still be taken that an upgrade or update in a microservice should not affect the other dependent service.
Enterprise readiness:
Microservices architecture can be considered as a conglomerate of different technologies. As technology is evolving day-by-day it is quite difficult to make a microservice application enterprise-ready as compared to conventional software.
Difference between Monolithic and Microservices architecture
| Parameters | Monolithic | Microservices |
| Type of system | Tightly coupled | Loosely coupled |
| Application development | Entire application is developed and deployed as one single unit. | The application is divided into different components which can be developed, packaged & deployed individually. |
| Codebase | A single and very large codebase with multiple modules for the entire application. | Multiple small-sized codebases. Each service has its own codebase. |
| Database | A single database is used for an application or a set of applications. | Each service has its own unique database or can use shared database but have different instances. |
| Development Teams | One large team responsible for developing and deploying application. | Each team can develop & deploy one or more components of the application individually. |
| Languages & Frameworks | Built with a small set of specific programming languages. | All services can be developed with different languages as per the need. |
| Testing | A monolithic application can be tested easily as the entire application is developed, deployed and scaled as a single unit. | Testing of a microservices application is difficult. To test one service, all the other services o which it depends needs to be launched. |
Sample Microservices architecture
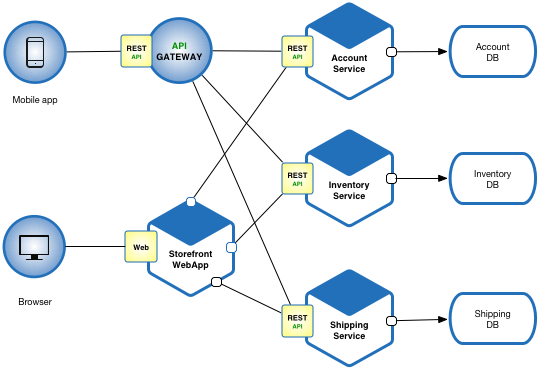
Let’s imagine that you are building an e-commerce application that takes orders from customers, verifies inventory and available credit, and ships them. As you can see in the image above, the application consists of 3 services namely:
- Account service
- Inventory service
- Shipping service
Each of these microservices can be accessed via an API Gateway (Mobile application) and web browser (Web application).
You can see that each of these services exposes a dedicated API and has its own unique database. This allows the services to communicate with each other only through their respective databases. Having such type of architecture allows more than one developers to make changes in the system.